Electric cars bring convenience to our travel, and are also loved by people for their energy-saving and environmentally friendly characteristics. However, have you ever considered how big a car is, how many amperes does it have? This article will delve into the ampere value of car batteries and the factors that affect battery performance.
How many amperes does a car battery have?
At present, the current of most car batteries is between 400–1000 amperes. Generally speaking, the larger the car, the higher the ampere rating. It should be noted that the ampere rating is not fixed and is easily affected by factors such as battery capacity, engine size and usage environment.
To understand the ampere rating of the vehicle battery, we can find the corresponding car model on the official website of the car manufacturer or in the accompanying manual.

What is the ampere rating of the car? What is the difference with the ampere value?
The ampere rating looks very similar to the ampere value. In fact, the two are different concepts, but they are both related to current.
Ampere refers to the amount of charge that passes through a conductor per second. For example, if our charger is 2 amperes, it means that 2 coulombs of charge flow into our mobile phone through the charger per second.
The ampere rating refers to the maximum current that an electrical device or electronic component can withstand under constant temperature and pressure. For example, many circuit breakers now have an ampere rating. When the current exceeds this rating, it will automatically trip to protect the safety of the circuit.
Therefore, the ampere value is actually the current size, and the ampere rating is the maximum current that an electrical or electronic component can withstand.
Through the previous content, we know that the ampere rating of a car battery will fluctuate, which involves the next link we need to discuss: the type of ampere rating of a car battery.
Types of ampere ratings of car batteries
Cold Cranking Current (CCA)
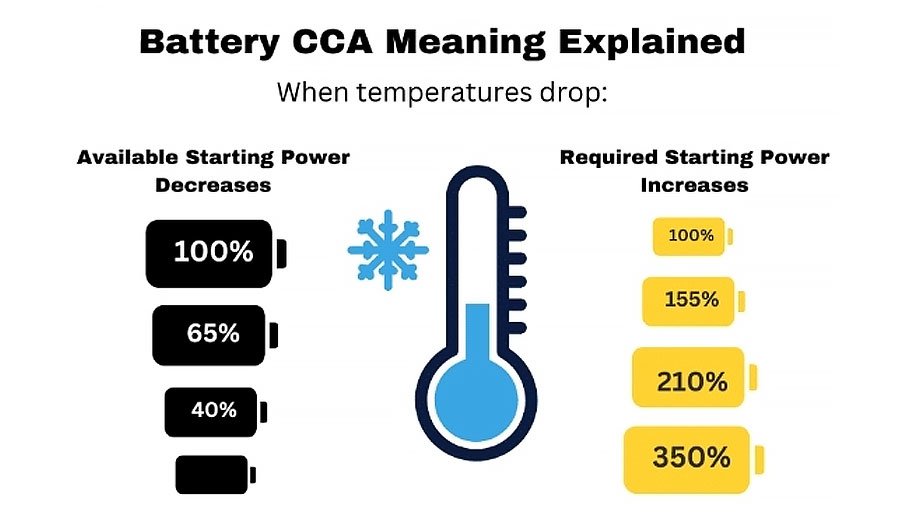
CCA is a common measurement method in the automotive battery industry and an important method to measure the performance of automotive batteries in low temperature environments. The specific test method is to place a 12-volt car battery at -17.8°C (0°F) for 30 seconds, record the continuous output current during this period, and the battery’s single cell voltage cannot be lower than 7.2 volts.
Most family cars currently have CCA values between 400-600, while larger vehicles such as vans and trucks usually have CCA values within 1000. Within a certain range, the greater the current output by CCA, the better the performance of the car.
However, if it exceeds this range, the excessive current of CCA may cause damage to the battery, resulting in some power loss.
Common CCA values of models:
- Chevrolet has a CCA of 590 amps
- BMW has a CCA between 575–600 amps (different models)
- Toyota Camry (large SUV) has a CCA of 750 amps
- Lincoln has a CCA of 852 amps
Reserve Capacity (RC)
Reserve capacity tests how long the car battery will continue to output 25 amps at a temperature of 26.67° (80°F) until the voltage drops to 10.5 volts. This is a test of how long the car battery can continue to power the electronic equipment on the vehicle after the alternator fails.
In other words, RC mainly tests the longest time that a car battery can last after a generator failure at room temperature. At present, most cars perform well and can last for 50–120 minutes. This period of time is enough for a faulty car to survive until the car repair point.
Ampere hour (Ah)
Ampere hour looks like a unit of measurement, which represents the rating of the total battery capacity and battery life. According to the regulations of the automotive industry, a standard car needs to reach 48 ampere hours, that is, it can provide 1 ampere of current within 48 hours.
Currently, all cars on the market exceed this standard. And the larger the size of the car, the higher the ampere hours it provides, such as vans and trucks basically exceed 75 ampere hours.
For cars with discharge functions, ampere hours are crucial, such as common RVs or hybrid cars. Higher ampere hours can be used for cooking food in the wild or for lighting.

How to measure the ampere number of a car battery?
In addition to checking the ampere number of a car battery on the official website of the car, we can also test the car ourselves. The test method is as follows:
- We set the multimeter to the switch for measuring DC voltage.
- Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal.
- After turning on the switch, the voltage will be displayed on the multimeter.
- Using Ohm’s law: Amperes = Volts / Resistance (Ohms), we can finally calculate the amperage.
What factors affect the ampere rating of a car battery?
From the above understanding, we all know that the ampere rating is basically tested at normal temperature and pressure, so in turn, there are some factors that affect it:
- Weather temperature: Overheated and overcooled weather will cause the battery’s ability to deliver current to decrease.
- Battery age: As the age of the car battery increases, its corresponding delivery capacity will also decrease, and it may even fail to provide the rated current.
- Battery status: The ability to deliver current is different when it is fully charged and not fully charged.
- Electrical load: The more electrical equipment a vehicle is equipped with, the more current it needs to provide.








