What is kw?
Kilowatt (kW) is a unit of electrical power, that is, the electrical energy generated or consumed by a certain item. If a light bulb consumes 100 watts per hour, then 10 light bulbs can consume 1000 watts per hour. The unit of kilowatt is mainly used to facilitate the calculation of the output power of some large electrical equipment.

What is kwh?
Kilowatt-hour is the energy consumed by an electrical appliance with a power of one kilowatt in one hour. Assuming that the light bulb above is still used as an example, it is equivalent to 100 light bulbs consuming 1000 watts per hour. The unit of kilowatt-hour is mainly used to better calculate the output power of large equipment after a period of use.
What is the difference between kw and kwh?
In order to help readers distinguish between the two concepts of kw and kwh, we have summarized 3 methods:
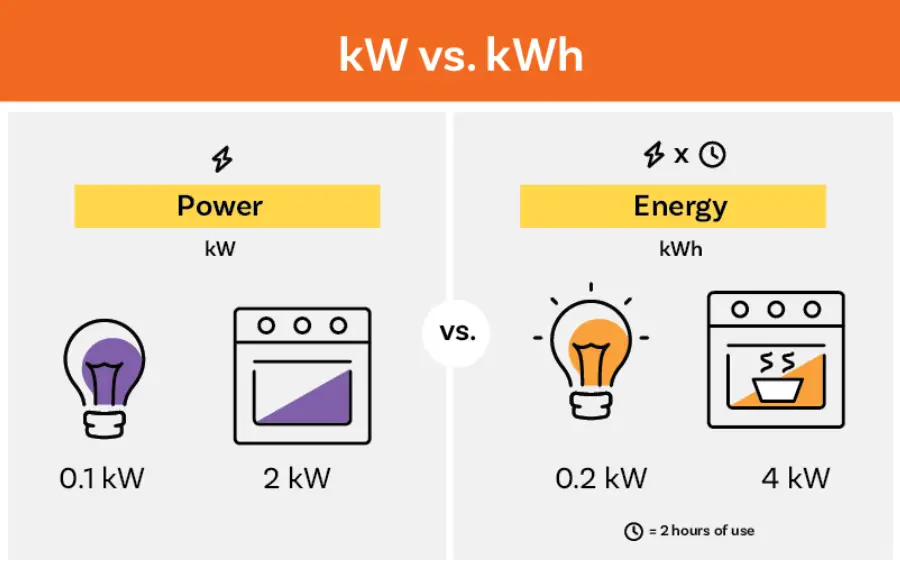
Different emphasis: kw is a unit of power, focusing on energy conversion. For example, a 7kw generator means that the rate of work done per unit time is 7kw. Kwh is an energy unit, focusing on the total energy consumed by the appliance in 1 hour. For example, if the charger of an electric car is 7kwh, it means that the charger can output 7kw of electricity in one hour.
Whether it involves specific time: kw has only 2 letters, while kwh has 3 letters, with the concept of h (hour). Therefore, we only need to see whether the unit carried involves specific time, such as 1 hour, 2.5 hours. When it involves specific time, kwh is used, otherwise, kw is used.
Practical application: kW tends to describe the performance of the equipment, while kWh tends to calculate and manage energy consumption.
Where do we use kw and kwh?
Application scenarios of kW (kilowatt)
Industrial production field
In factories, kw is usually needed to measure the power of various equipment, especially when there are multiple large equipment in the factory, the total power of all equipment needs to be calculated in order to equip a suitable distribution cabinet to control and ensure the operation of all equipment.
Automotive field
The power of automobile engines is also often expressed in kW, and the higher the power of automobile engines, the better its performance. The engine power of many high-performance cars is usually above 300kw. In addition, when we calculate fuel loss, the power of the engine is also an important parameter that cannot be obtained.
Power equipment field
Conventional generators, transformers and other equipment all use kw to express their capacity, representing the maximum power it can provide. For example, a 7kw engine, then the maximum power it can provide is 7kw.
By understanding the maximum power, users can choose the most suitable power equipment so that they can ensure the normal power supply of electrical equipment when there is a power outage or in the wild.
Application scenarios of kWh (kilowatt-hour)
Household electricity metering
The unit used by the electricity meter commonly used in our homes is kWh. The power company also charges according to this value. Users can also estimate the power consumption of all electrical appliances in an hour. For example, a 2kw electric kettle is used for 10 minutes, so the power consumption is 0.33kwh.
Commercial building energy consumption assessment
For commercial buildings such as office buildings, shopping malls, and cinemas, it is necessary to use kwh to evaluate the energy consumption of all electrical equipment in the building, and then design energy-saving plans to reduce operating costs.
Energy production and distribution
The power generation and distribution of power plants are also carried out in kWh. By systematically analyzing kwh data and adjusting it, ensure that electricity can be supplied for a long time.
How to use kilowatts and kilowatt-hours in electric vehicle chargers
When we charge an electric vehicle, the charging rate is expressed in kilowatts, and the actual energy used is calculated in kilowatt-hours. For example, when charging at a public charging station, the charging station will charge per kWh used.
In addition, chargers with different output power will determine the time and cost we pay. For example, if we choose a 22kw electric vehicle charger, it will be 2 times faster than a 7kw electric vehicle charger. Therefore, choosing the right charger and charging strategy plays an important role in our cost savings.
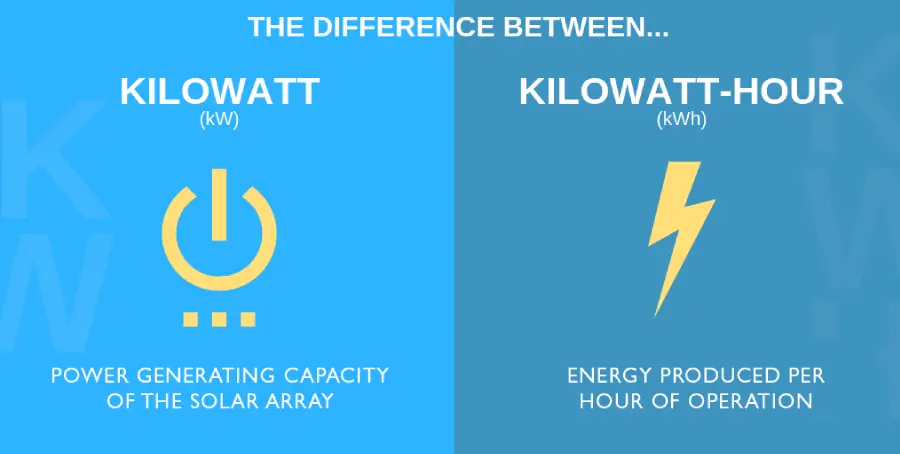
How to use kilowatts and kilowatt-hours in solar power generation
In solar power generation, kw and kWh are important factors affecting the quotation. Generally speaking, the size of the system is quoted in kW, while the expected annual energy output is quoted in kWh, and the quotations between the two are quite different.
The energy output of a solar array is estimated based on the following factors:
- System size (kW)
- The peak sunshine hours per day at the location
- Any shadows that affect power output
- The conversion efficiency of the solar inverter