What is Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE)?
Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) is the core component of an electric vehicle charging station, so some people mistakenly regard EVSE as an electric vehicle charging station. In fact, the two are not exactly the same. We will explain this in detail later.
Simply put, EVSE is a device that connects the power grid and electric vehicle charging. It helps electric vehicles to be fully charged by obtaining power from the power grid and then transmitting it to electric vehicles.
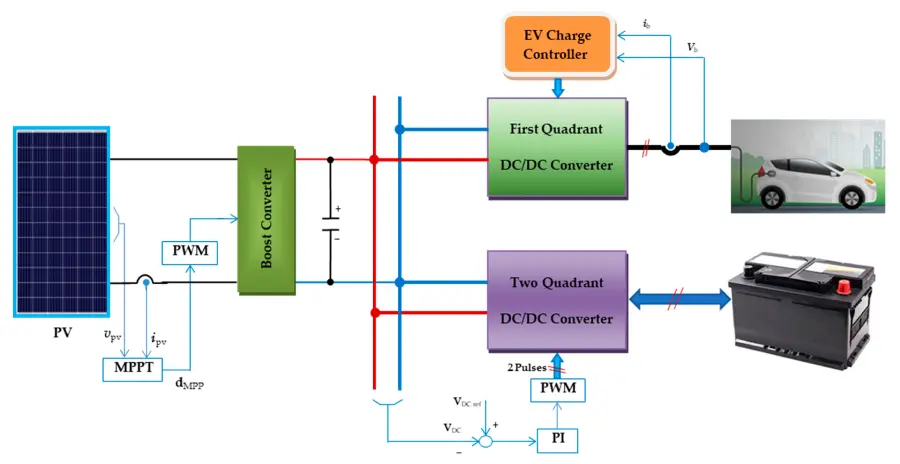
How does an EVSE work?
Although EVSE looks unfamiliar, its working principle is very simple. Let’s learn about it together.
When the electric vehicle charger is plugged into the EVSE device, EVSE needs to analyze the current type of electric charger (such as Level 1 (slow charging), Level 2 (fast charging) and Level 3 ( DC fast charging)), and then adjust the output current of the power grid according to the vehicle battery load.
The working principle of EVSE is generally still a way to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), so as to help electric vehicles better complete the charging function.
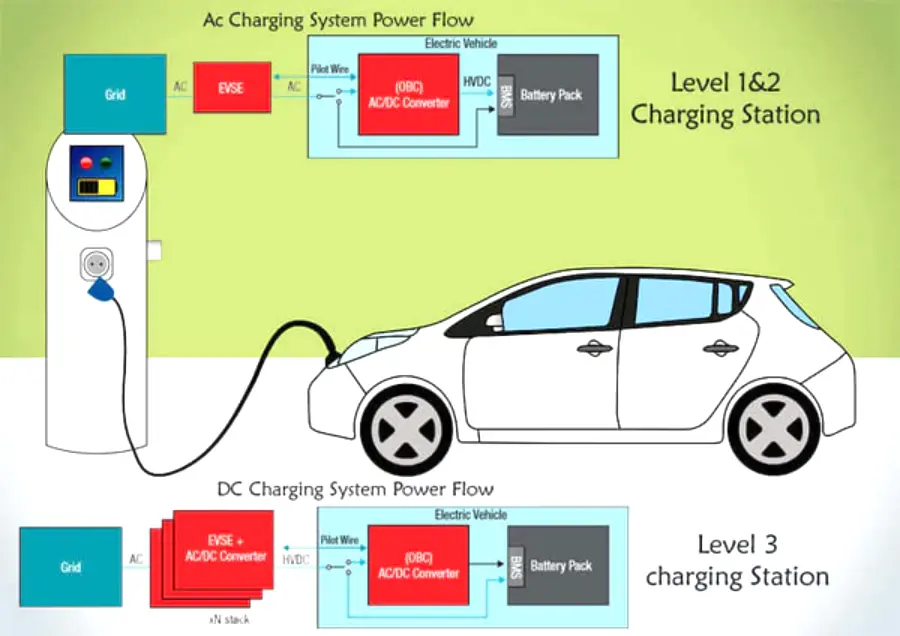
Components of EVSE
EVSE is a complete set of equipment, and it will be slightly different depending on the type (such as home charging pile or public charging station), but the overall components are similar. Let’s take a look at them one by one:
Shell
The shell of EVSE is mainly to protect the internal components from the environment or other external forces. EVSE has different shells depending on the installation scenario. There are two types of home charging piles: wall-mounted and base-mounted. They look like a small box, while public charging piles are obviously much larger and more like a large iron cabinet.
Electronic components
Although the external shape of EVSE is different, the internal electronic components are similar, including: main relay (turning on and off the charging current), control module (controlling charging time, output power, etc.), power supply (powering the internal electronic components), charging socket, indicator light and optional user operation interface.
Firmware
EVSE firmware can be understood as an operating software or vehicle system, which mainly provides various functions for EVSE, such as controlling the electric vehicle charging pile to start or stop charging, obtaining and recording the current charging status in real time, etc. The firmware can be updated or expanded at any time through the cloud.
Electric vehicle charging level
The levels of electric vehicle connectors are relatively complex. According to their types, they are currently mainly divided into level 1, level 2 and level 3 chargers. Let’s take a look at them separately:
Level 1 charger
- Voltage and power: Level 1 chargers use 120 volts AC, and the output power is between 1.4 kW and 1.8 kW.
- Charging speed: Due to the low output power of the Level 1 charger, it usually takes 20 to 45 hours to fully charge, depending on the different brands of electric vehicle batteries.
- Applicable scenarios: Level 1 chargers are mainly used for home charging, especially for charging at night.
- Cost and installation: Level 1 chargers generally use home sockets directly, without the need for additional scene construction, simple installation, and low cost.
Level 2 charger
- Voltage and power: Level 2 chargers use 240 volts of AC power, and the output power range is between 3.3 kW and 19.2 kW.
- Charging speed: Compared with Level 1 chargers, Level 2 chargers are obviously much faster, and most electric vehicles can be fully charged within 3 to 8 hours.
- Applicable scenarios: Level 2 chargers are generally considered to be a fast charging method, more suitable for workplaces, hotels, supermarkets and other places.
- Cost and installation: Level 2 chargers have a higher output power, and usually require professional electricians to install, which is significantly more expensive.
Level 3 charger (DC fast charger)
- Voltage and power: Level 3 chargers use DC power, and the output power ranges from 50 kW to 400 kW.
- Charging speed: Level 3 chargers offer the fastest speed, and most can fully charge the battery in 30-50 minutes.
- Applicable scenarios: Level 3 chargers are mainly used in scenarios that require fast charging, such as gas stations, parking lots, etc., suitable for long-distance travel and fast charging needs.
- Cost and installation: Level 3 chargers are expensive, and installation costs are also high, requiring dedicated infrastructure support.
Network connection
The EVSE device has a built-in network connector, which allows us to use the mobile phone’s wifi or cellular network to unlock and use the device. Some also support scheduled charging, and after the countdown ends, it will automatically enter the charging state.
Power access
It is mainly to connect the EVSE device to the power grid. Different levels of current output have different supporting power facilities. Detailed information can be obtained from the local power grid company.
What is the difference between EVSE and electric vehicle charging piles?
Although both EVSE and electric vehicle charging piles can provide power for electric vehicles, we can see from the above introduction that EVSE covers the entire charging system, including hardware and software, while electric vehicle charging piles usually refer to specific charging equipment or stations.








