Nowadays, there are many kinds of AC chargers in the market, how to choose the right charger for you is especially important.
1.Understanding voltage and current
Current and voltage are important features of AC charging, power is equal to current x point voltage, current and voltage affect charging power, and charging power affects charging speed.
Amperage is the amount of electricity that can pass through a wire at any given time. Higher amperage means that power can be transferred to the end device faster.
The cable used will determine the current strength of the charger. The fastest charge is likely to have the highest voltage and the highest amperage.
2.Understanding the charging standards
Now the main charging interfaces on the market are type 1, type 2, GBT, NACS, these standards have corresponding chargers, type 1 standard is mainly in the U.S., type 2 standard is mainly in Europe, GBT is mainly in China and Southeast Asia, NACS is mainly in the U.S. With the flow of the market and trade, these standards exist in various places, we have the corresponding adapters to convert between the various standards, such as type 1 to GBT, type 2 to type 1, and so on.
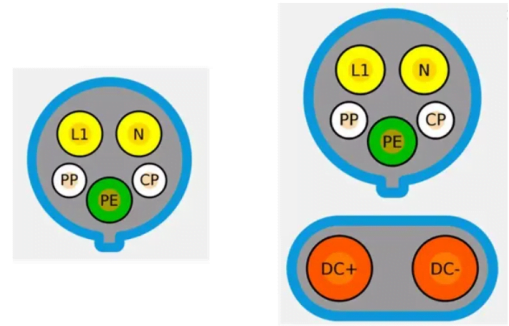
1.SAE J1772 standards
The North American charging standard is mainly used in the United States and Canada, with a maximum AC voltage of 240V AC and a maximum current of 80A AC; and a maximum DC voltage of 1000V DC and a maximum current of 600A DC now.
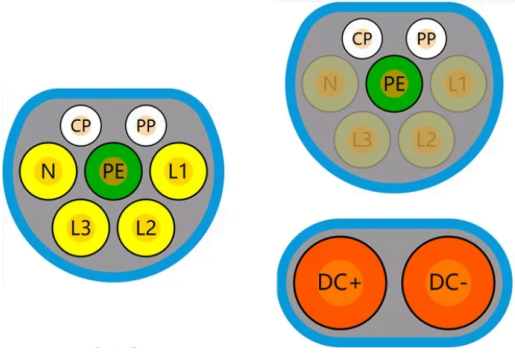
2.IEC 6296 type 2 standards
The voltage range in Europe is about the same as in China, and the charging interface, CCS2, is the same as the US standard, CCS1, but there are some variations. The main difference is that the standard household electricity in Europe is 230 volts, almost twice the voltage used in North America, so there is no Level 1 charging in Europe. The European standard AC maximum voltage is 480V AC with a maximum current of 63A; the DC maximum voltage is 1000V DC with a maximum current of 600A DC with cooling.
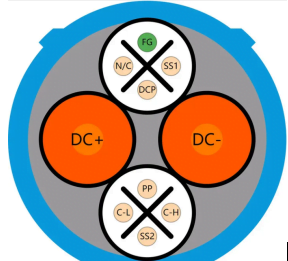
3.Japan Standard CHAdeMO Charging Standard
Japan’s charging standards are unique in that AC is governed by the American Standard J1772, while DC is governed by the CHAdeMO standard.J1772 has already been mentioned, so let’s focus on the CHAdeMO standard.
CHAdeMO is a DC plug jointly developed by five Japanese automakers and attempted to promote it as a global standard from 2010, but it has not been widely adopted. Nonetheless, there are a number of countries or regions that have adopted the CHAdeMO interface, and apart from Japan, most of these installations are in Europe (with a predominance of Scandinavia), the United States and South Korea. There are two versions of the CHAdeMO standard, the first version supports charging up to 62.5 kW with a maximum current of 125 A, while the revised CHAdeMO 2.0 specification allows for up to 400 kW. Meanwhile, the CHAdeMO Association is working with China to develop an ultra-fast connector capable of charging up to 900 kW, also known as the Chaoji charging interface.
4.NACS charging standards
The common charging standard in the US is J1772, the only exception being Tesla, which has developed its own dedicated charging port for charging Tesla electric cars. Tesla announced its own NACS standard on 11 November 2022 and welcomes everyone to use it.
NACS is an AC/DC integrated socket, and due to the limitations of the interface, NACS also has a limitation in that it is not compatible with having AC three-phase power. This makes it impossible to be used in countries or regions where three-phase AC power is used, such as China and Europe.
The interface circuit of NACS is exactly the same as the interface circuit of CCS, so for the original CCS standard interface of the on-board control and detection unit (OBC or BMS) circuit, there is no need to re-design and layout, and it is completely compatible. This is favourable to the promotion of NACS.
Of course, there is no restriction on communication and it is fully compatible with the requirements of IEC 15118.
The maximum voltage of NACS is 1000V DC and the maximum current is 400A DC; AC is consistent with J1772.

5.GBT Charging standards
China’s electric vehicle standard charging interface and handshake circuit of the reference standard part, respectively, GB/T 20234 and GB/T 18487.1. which the maximum voltage of AC charging interface for three-phase 440V AC, the current of the maximum 63A AC; and DC charging of the maximum voltage of 1,000V DC, the current of the maximum 300A DC in the natural cooling, the current of the maximum current in the active cooling of the 800A DC
6.adapters to support kinds of charging station
Due to the mobility of vehicles and the fixed nature of public charging posts, it is often the case that the charging post is not suitable for the vehicle and thus the charging is not possible, we have several adapters to solve this problem.
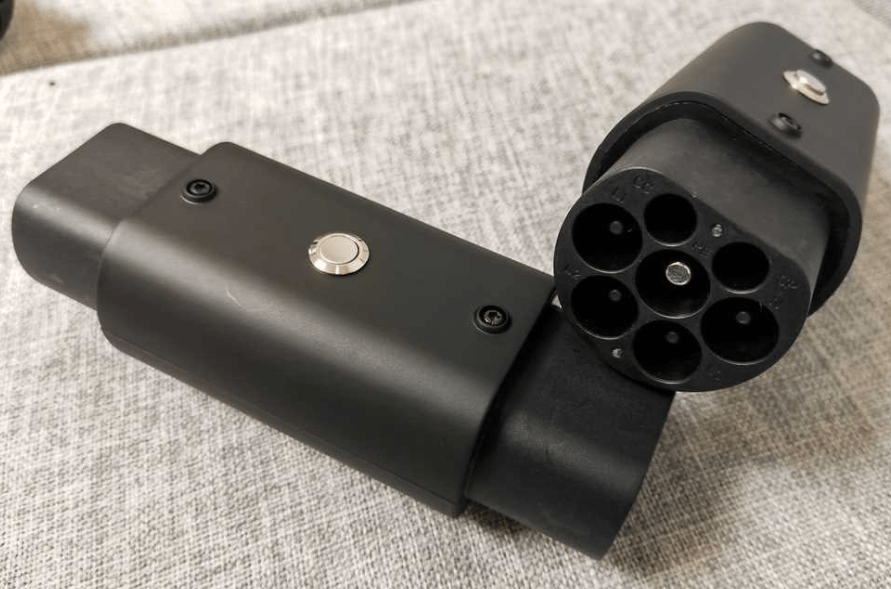

Type 1 to type 2 adapter:type 2 car charge on type 1 stations, the stations with type 1 cables.
type 2 to type 1 adapter: type 1 car charge on type 2 stations.
type 1 to GBT adapter: GBT car charge on type 1 station, the stations with type 1 cables.
Type 2 to GBT adapter: GBT car charge on type 2 station, the stations with type 2 cables.
Tesla (NACS) to GBT adapter: GBT car charge on NACS station.
Type 2 to Tesla (NACS) adapter: Tesla car charge on type 2 station.
Tesla(NACS) to Type 2 adapter: type 2 car charge on NACS station.
Telsa(NACS) to type 1 adapter: type 1 car charge on NACS station.
3.Charging environment
Chargers are used under different conditions, some are used indoors, such as charging posts in car parks, portable chargers used at home, etc. The waterproof rating of these chargers does not need to be particularly high, IP54 is already sufficient, and those with lower waterproof ratings cost less.
Some chargers need to be installed outdoors, or portable chargers that are placed in the car ready to charge, these need high waterproof performance and UV protection, and usually need the charger to be able to withstand the heat and cold. Chargers for outdoor use require a higher level of protection than those for indoor use, and are usually slightly more expensive.
Our portable chargers waterproof class is IP67, It has been tested by authorised laboratories for water resistance and can also withstand temperatures of -40 and +85 degrees Celsius, it can suitable for outside use.
4.Smart ac charger is important
There are very many chargers on the market now and it is important to identify and choose a smart charger as this can make charging safer and more efficient
The use of smart chargers will effectively improve the charging efficiency of electric vehicles, thus saving time and fuel. Because the smart charger adopts an intelligent control system, so that the charging speed can be adjusted in time according to the electric power of the electric car, and the charging of the electric car can be completed more effectively, thus saving time and fuel.

The smart charger can ensure the electric car’s power and battery life. The smart charger can automatically cut off the power according to the battery level, thus effectively guaranteeing the safety of the battery, preventing overcharging and overdischarging of the electric car, and effectively prolonging the service life of the battery.
Smart chargers can provide assurance of a safer environment. As the smart charger has advanced electronic circuit design, it can integrate and control the safety key. When it detects low temperature, high voltage, interference from external electromagnetic waves, etc., the vehicle will suspend charging to ensure the safety of the electric vehicle.
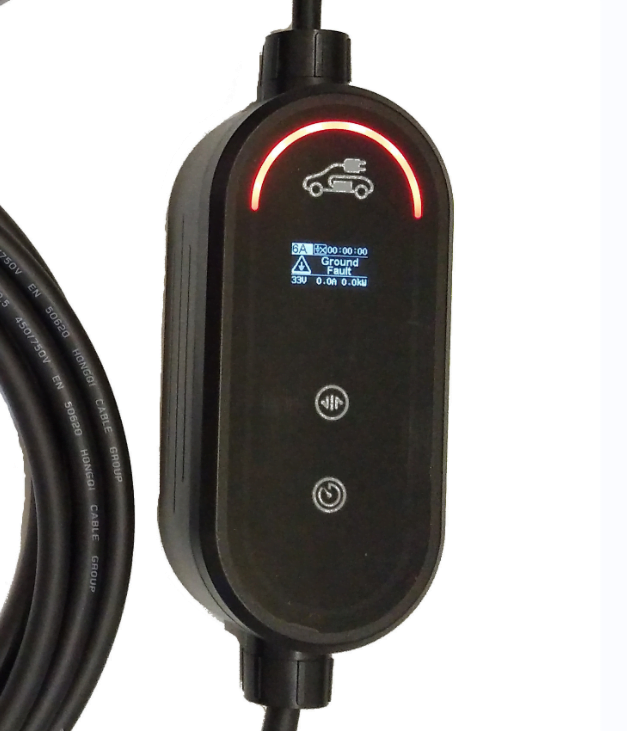

Scheduling charging sessions to improve efficiency Smart EV chargers can optimise charging sessions according to user preferences, grid conditions and energy rates to ensure efficient use of energy and reduce charging time, e.g. arrive home from work at 6pm and book a charging appointment to start charging 6 hours later, which is the cheapest time period for grid costs.
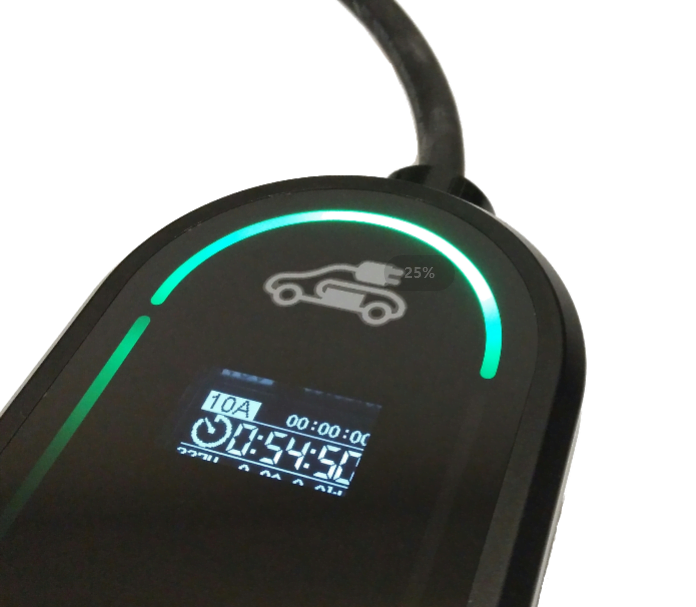

The benefits of the smart charger for electric vehicles are obvious, it can detect the charging status of the battery, and can obtain the working voltage and temperature of the battery during the charging process in real time, so as to improve the safety and reliability of electric vehicles. At the same time, the smart charger can also achieve overcharge, overdischarge, short-circuit and other protection functions, in order to reduce the emergence of short-circuit or over-charging of the battery of the electric car, etc., to protect the battery, to avoid the occurrence of dangerous accidents, and effectively improve the charging safety.







